Hot Spots on Photovoltaic Panels: Causes, Effects, and Prevention
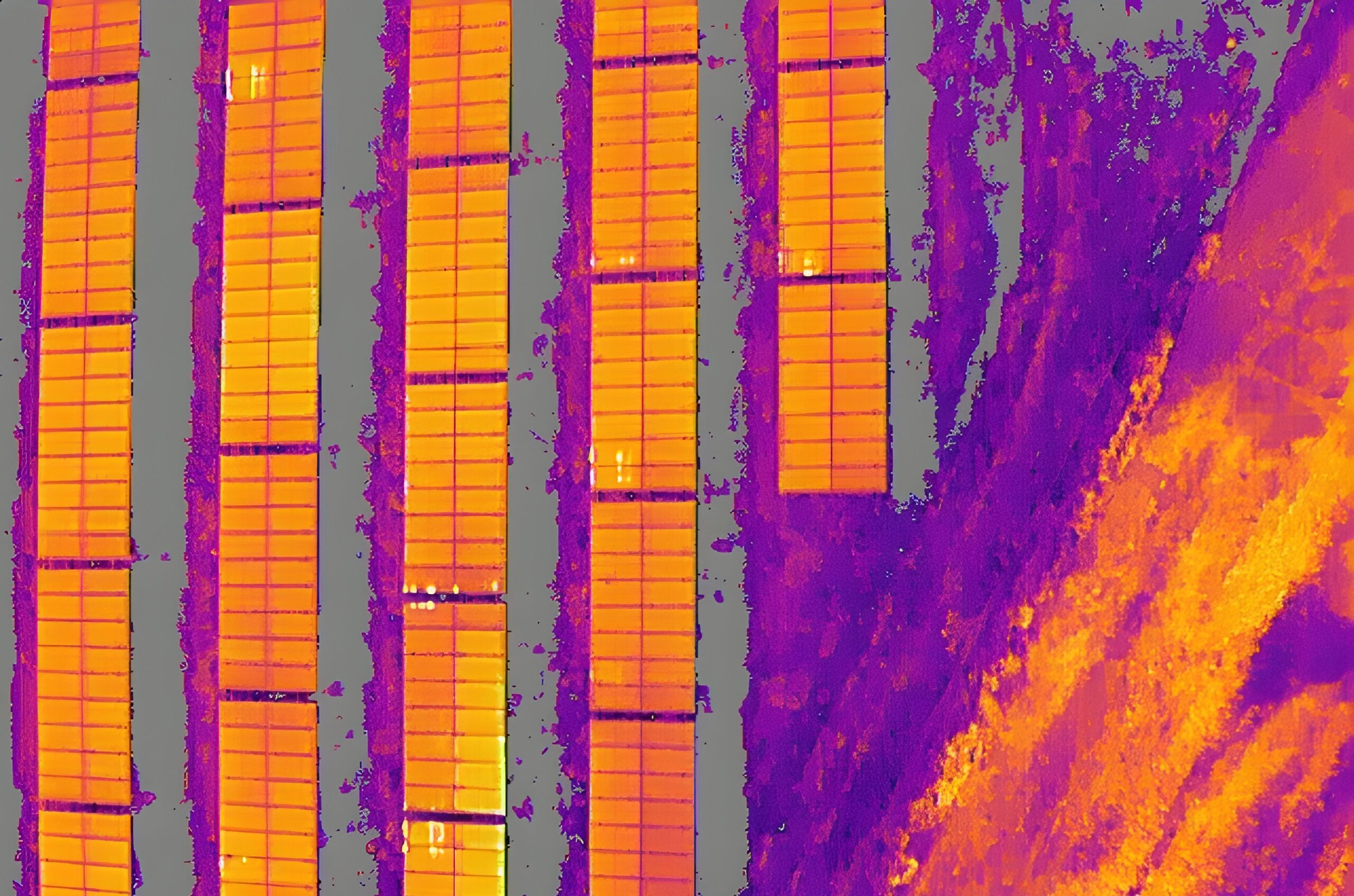
Hot spots are localized areas of elevated temperature on photovoltaic (PV) panels that can lead to irreversible damage if not addressed promptly. Understanding the causes of hot spots, particularly their association with high vegetation and shading of PV panels, is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of solar energy systems. In this article, we will explore the formation of hot spots on PV panels, their implications, and strategies for prevention.
Causes of Hot Spots on Photovoltaic Panels
Hot spots can be caused by various factors, including:
- High Vegetation Density: Overgrown vegetation around PV panels can obstruct sunlight, leading to shading of certain cells or sections of the panel. Shaded cells can become “reverse-biased,” causing them to dissipate energy in the form of heat rather than generating electricity.
- Partial Shading: Partial shading of PV panels due to nearby objects such as trees, buildings, or debris can create significant temperature differentials across the panel surface. This temperature variation can induce hot spots in the shaded areas, particularly during peak sunlight hours.
- Module Mismatch: Mismatch between PV modules within an array, either due to manufacturing variations or partial shading, can exacerbate hot spot formation. In mismatched arrays, shaded modules may act as “sinks” for the current generated by unshaded modules, leading to localized heating and hot spot formation.
Effects of Hot Spots
The presence of hot spots on PV panels can have several detrimental effects, including:
- Reduced Efficiency: Hot spots decrease the overall efficiency of the PV system by dissipating energy as heat rather than converting it into electricity. This can lead to decreased power output and lower energy yields over time.
- Cell Degradation: Prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures can accelerate the degradation of PV cells, resulting in reduced performance and shortened lifespan of the panels.
- Risk of Fire: In extreme cases, hot spots can reach temperatures high enough to pose a fire hazard, especially if flammable materials are present in the vicinity of the PV system.
Preventing Hot Spots
Preventing hot spots requires proactive measures to minimize shading and optimize the performance of PV panels:
- Vegetation Management: Regular maintenance and trimming of vegetation around PV panels can reduce shading and minimize the risk of hot spot formation.
- Optimal Panel Placement: Careful planning of panel placement to minimize shading from nearby objects and maximize exposure to sunlight can help prevent hot spots.
- Module-Level Electronics: The use of module-level power optimizers or microinverters can mitigate the impact of partial shading and module mismatch, thereby reducing the likelihood of hot spot formation.
Conclusion
Hot spots pose a significant risk to the performance and reliability of photovoltaic panels, particularly in environments with high vegetation and shading. By understanding the causes of hot spots and implementing preventive measures such as vegetation management and optimal panel placement, solar energy system owners can ensure the long-term viability and efficiency of their installations.
